

Apply more DEET to boots, socks, and pant legs below the knees. Tuck pant hems into socks and run a band of duct tape around the seam. Stripes below the bottom edge of your underwear on the upper thighs and around each leg below the knee ensure that the tick and chigger recon squad can’t move up or down. Pull up your shirt and run a stripe around your waist an inch above where your pants ride. Stripes above and below the elbow and around your wrists keep creepies from crawling up your arms. For skin, use Deet, picardin, oil of lemon eucalyptus, IR3535, or 2-undecanone. The best tick-proofing for clothing is to spray it with a solution containing 0.5 percent permethrin.
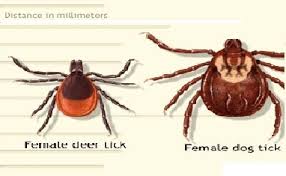
WOOD TICK VS DEER TICK SKIN
After being outside, check the areas where ticks like to attach, which is anyplace where your skin is thin, including your ankles, backs of knees, around the waist, between the legs, underarms, hairy areas, and in or around the ears. CDCįor us, the experts recommend wearing light-colored clothes, which makes it easier to spot ticks. A deer tick grows to more than three times its original size after 96 hours of sucking your blood. Well, that advice is fine for plenty of people, but not for hunters and ambitious fishermen. Or, if you must be outside, walk in the middle of trails. If you want to keep them off you, the Centers for Disease Control says you should avoid heavily wooded or brushy areas with high grass and leaf litter. You don’t have to go to the woods to find ticks.
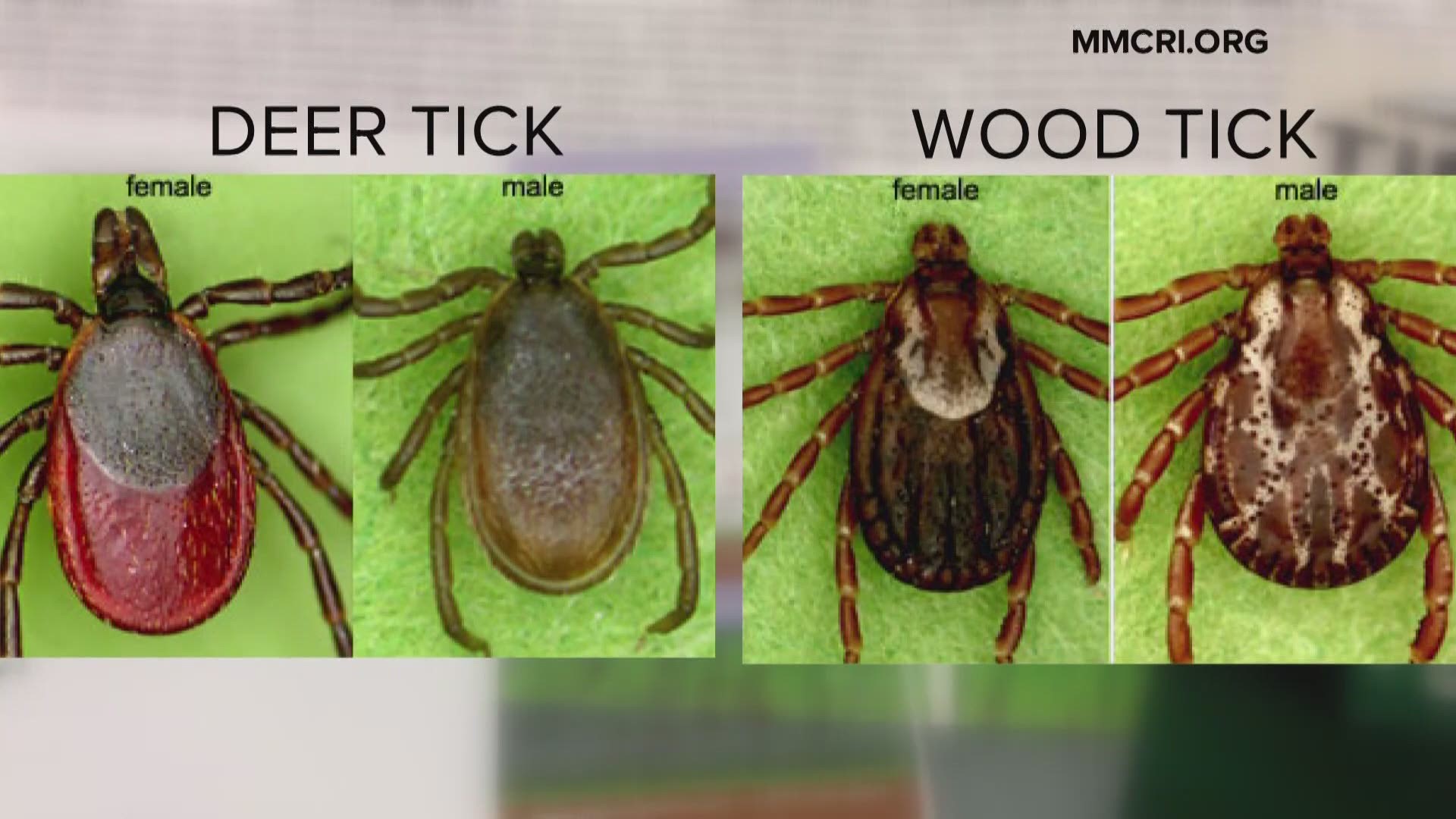
WOOD TICK VS DEER TICK HOW TO
How to Avoid Ticks (and Keep Them from Sucking Your Blood)

CDC Lyme Disease and Other Tick Borne Diseases A deer tick’s life cycle from larva to adult. That takes place when their saliva becomes infected and is passed back into the host as they eat your blood. It’s thought that ticks need to be attached for 24 to 48 hours before they can transmit and infect. A tick even secretes a cement-like substance through its saliva to keep itself glued to the host. That’s a lot more intimacy than I’m comfortable with. While ticks in the larval and nymph stage attach for 3 or 4 days, an adult female will stick to its host for up to 10 days. While most biting pests-like mosquitoes-take a bite and move on, a tick buries its curved teeth into a host and stays there for days. A tick seeks its host by crawling up brush or a blade of grass and hanging out there with its front legs splayed in the air, just waiting for a warm-blooded critter to pass by. What Are Ticks and How do They Feed? A female deer tick questing-that is, reaching and waiting to cling to any suitable host that happens by. In this story, we’ll take a look at the five ticks you need to watch out for, the diseases they cause, and how to avoid the little bloodsuckers in the first place. This makes it even more difficult than normal for doctors trying to diagnose and treat Lyme and other tick-borne diseases. (A “vector-borne” disease is passed from one organism to another.) Further, the geographic ranges of many tick species are expanding, driven both by climate change and changing land-use patterns.Ĭomplicating things right now is the fact that the flu-like symptoms of many tick-borne diseases mimic those of Covid-19. Ticks are now the number one vector-borne cause of disease in this country. Between 20, reports of tick-borne diseases more than doubled in the U.S., a trend that experts say continues. It’s a good time to be a blood-sucking parasite, and not just as a member of the U.S. We may earn revenue from the products available on this page and participate in affiliate programs.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
